Discovering Alendronate: Early Research and Development
As we take a look back at the history of alendronate, it's important to start at the very beginning – the initial research and development of this groundbreaking drug. The story of alendronate begins in the 1960s, when scientists were eager to find a solution for osteoporosis, a debilitating disease characterized by weak and fragile bones. It was during this time that researchers discovered bisphosphonates, a class of compounds that showed promise in preventing bone loss.
The first bisphosphonate to be synthesized was etidronate, which was found to inhibit bone resorption by disrupting the action of osteoclasts – the cells responsible for breaking down bone tissue. While etidronate was successful in slowing down bone loss, it also had some limitations, including a tendency to cause mineralization defects in bones. This led researchers to continue their pursuit of an even more effective bisphosphonate.
Alendronate: A New Generation of Bisphosphonates
In the 1970s, alendronate was developed as a second-generation bisphosphonate. This new compound was designed to have a more potent inhibitory effect on osteoclasts while avoiding the unwanted side effects associated with etidronate. Alendronate showed great promise in preclinical studies, as it not only inhibited bone resorption but also stimulated bone formation, leading to an overall increase in bone density.
As research on alendronate continued, it became evident that this new bisphosphonate had the potential to revolutionize the treatment of osteoporosis. The combination of anti-resorptive and pro-formative properties made alendronate a prime candidate for clinical trials, and in the 1980s, the first studies involving human subjects were conducted.
Fosamax: The Introduction of Alendronate to the Market
After years of research and clinical trials, alendronate was finally approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1995 under the brand name Fosamax. Developed by Merck & Co., Fosamax was the first bisphosphonate drug to receive FDA approval for the treatment of osteoporosis. This marked a significant milestone in the history of alendronate, as it became available to millions of people suffering from this debilitating condition.
With its proven efficacy in reducing the risk of fractures and increasing bone density, Fosamax quickly gained popularity among healthcare providers and patients alike. The introduction of a once-weekly dosing regimen in 1999 further increased the drug's appeal, making it more convenient for patients to adhere to their treatment plans. Fosamax remained the leading osteoporosis medication in the market for many years, until the introduction of newer bisphosphonates and other treatment options.
Alendronate in the 21st Century: Continuing Research and Development
As the new millennium began, researchers continued to study alendronate in order to gain a better understanding of its long-term effects and potential applications beyond osteoporosis. Studies were conducted to explore the use of alendronate in treating other bone-related conditions, such as Paget's disease and glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis.
In addition to exploring new indications, scientists also investigated the optimal duration of alendronate treatment. It was discovered that, in some patients, the benefits of alendronate could be maintained even after stopping the medication. This finding led to the concept of a "drug holiday," in which patients could take a break from their bisphosphonate treatment without experiencing a significant decline in bone density.
Challenges and Controversies Surrounding Alendronate
Despite its undeniable success in treating osteoporosis, alendronate has not been without its challenges and controversies. In the early 2000s, concerns arose about the potential link between long-term bisphosphonate use and rare but serious side effects, such as atypical femoral fractures and osteonecrosis of the jaw.
These concerns prompted further research into the safety of alendronate and other bisphosphonates, leading to updated guidelines and recommendations for their use. While the benefits of alendronate still largely outweigh the risks for most patients, healthcare providers are now more cautious in prescribing the drug, taking into account individual risk factors and closely monitoring patients during treatment.
The Future of Alendronate: New Developments and Applications
As we look towards the future of alendronate, it's clear that this groundbreaking drug will continue to play an important role in the management of osteoporosis and other bone-related conditions. Ongoing research is focused on optimizing the use of alendronate, such as determining the ideal duration of treatment, identifying patients who would benefit most from the drug, and exploring the potential of combination therapies with other medications.
With new developments and applications on the horizon, the history of alendronate is far from over. As we continue to learn more about this remarkable drug, it's exciting to think about the potential impact it could have on improving the lives of countless individuals affected by bone diseases around the world.

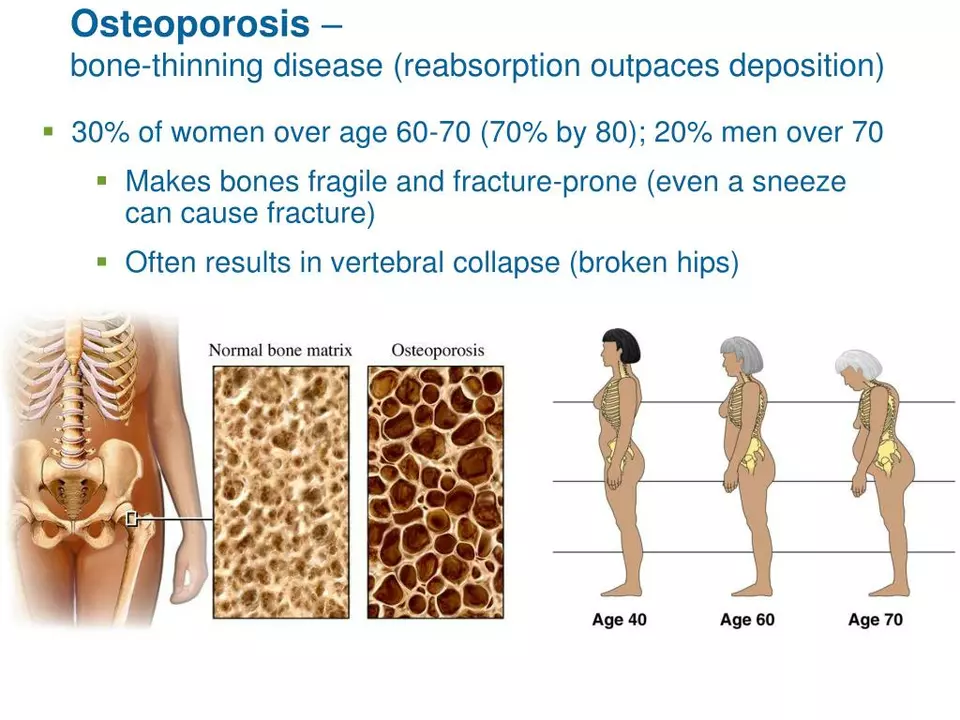
16 Comments
Heather ehlschide
Alendronate’s journey from the 1960s bench work to the Fosamax launch shows how incremental chemistry can reshape patient care, especially for those at high fracture risk.
Kajal Gupta
Wow, reading about alendronate feels like flipping through a sci‑fi novel where the heroes are bone cells and the villains are tiny cracks – truly a kaleidoscope of discovery! 🌈
Zachary Blackwell
Don’t you think it’s odd how the “breakthrough” narrative around Fosamax conveniently coincided with big pharma’s lobbying surge? It’s as if the drug was engineered not just for bones but for bank balances.
prithi mallick
i cant help but wonder wht it mehns for the future when we keep putting these medicnes in bodies without fully knwoing long term effects. alendronate was a gamechanger but also a reminder of how much we still lern.
Michaela Dixon
Alendronate started as a curiosity in a lab looking for ways to stop bone loss. Researchers in the 1970s tweaked the molecular structure and saw a stronger effect on osteoclasts. The drug showed promise in animal models before any human trials began. By the early 1980s, a handful of clinical studies were launched to test safety. Patients reported fewer fractures after months of weekly dosing. The FDA approval in 1995 marked the first bisphosphonate sanctioned for osteoporosis. Fosamax quickly became a household name among endocrinologists. The convenience of a once‑weekly pill boosted adherence compared to daily regimens. Over the next decade, the market saw a surge in bisphosphonate prescriptions. However, rare side effects like jaw osteonecrosis raised alarms. Doctors began recommending drug holidays after five years of use. Some patients switched to alternative therapies such as denosumab. Ongoing studies explore alendronate’s role in Paget’s disease. Others look at its potential in preventing metastasis‑related bone loss. The conversation now includes personalized treatment duration. In the end, alendronate’s legacy is a mix of triumphs and cautionary lessons.
Dan Danuts
Great rundown! It’s amazing how a single molecule can shift an entire treatment paradigm – keep the science rolling!
Dante Russello
Indeed, the development of alendronate represents a pivotal moment in osteoporosis therapy; a testament to decades of meticulous research, rigorous clinical trials, and collaborative effort across institutions; its impact on fracture reduction is undeniably significant, and the subsequent refinements in dosing schedules have enhanced patient compliance dramatically.
James Gray
Yo, alendronate is legit – it helped my grandma stop breakin her hip. No joke, the weekly pill is super easy.
Scott Ring
The story of alendronate illustrates how scientific perseverance can translate into real‑world health benefits, bridging the gap between laboratory breakthroughs and everyday patient outcomes.
Shubhi Sahni
Alendronate’s trajectory-from early bisphosphonate research, through FDA approval, to contemporary debates on drug holidays-is a fascinating case study; it underscores the importance of ongoing pharmacovigilance; it also highlights the dynamic nature of clinical guidelines.
Danielle St. Marie
Honestly, this drug shows how American pharma can dominate global markets; while other countries lag behind, we set the standards – 🇺🇸💊
keerthi yeligay
Alendronate is a key part of bone health regimen but need careful monitoring.
Peter Richmond
The evolution of alendronate underscores the value of evidence‑based therapy in osteoporosis management.
Bonnie Lin
Alendronate changed osteoporosis treatment forever
sara fanisha
Love seeing how far we’ve come with bone meds – hope the next wave is even better!
Tristram Torres
Alendronate has both benefits and risks that need to be weighed carefully.