Automated Dispensing Cabinets: How They Improve Medication Safety in Hospitals and Pharmacies
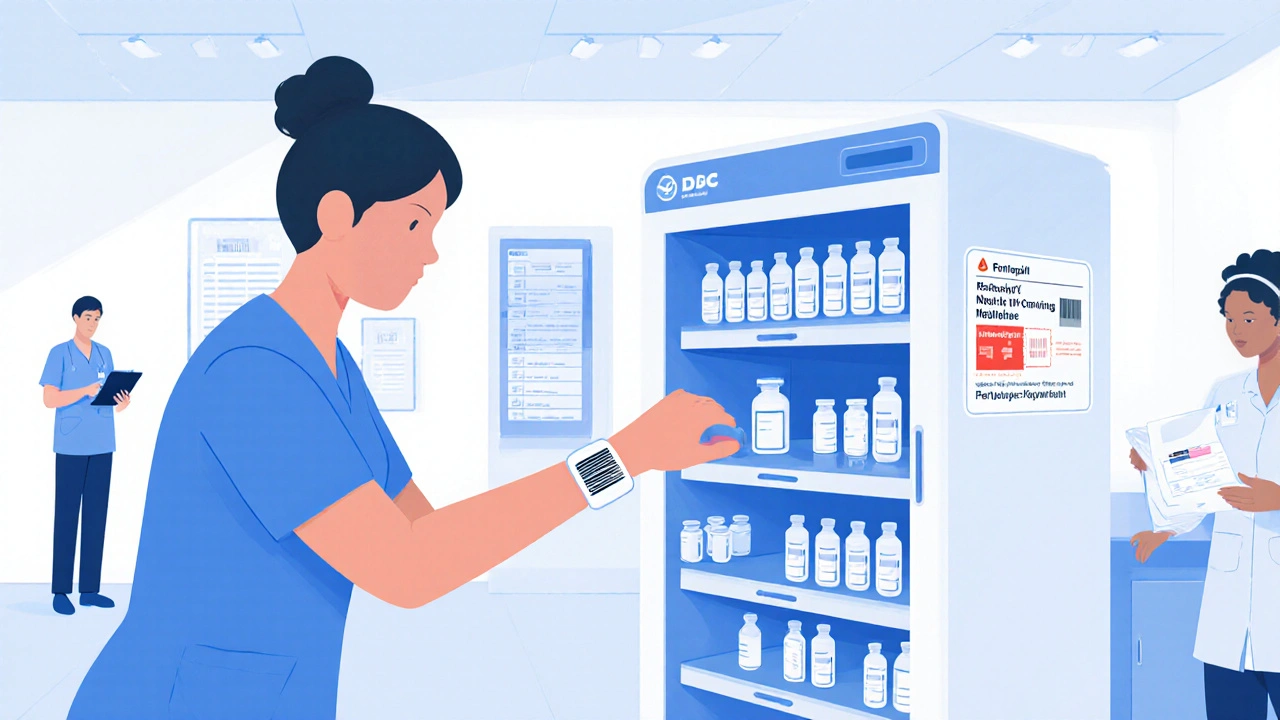
When you think about how medications get from the pharmacy shelf to a patient’s bedside, you might picture a pharmacist handing over a pill bottle. But in most hospitals, that’s not how it happens anymore. Automated dispensing cabinets, computer-controlled devices that store and dispense medications securely in clinical settings. Also known as madison cabinets or drug dispensing systems, they’re now standard in nearly every hospital pharmacy and nursing unit. These aren’t just fancy vending machines—they’re part of a system designed to cut down on medication errors, prevent theft, and give nurses real-time access to the right drugs at the right time.
Automated dispensing cabinets work by linking to the hospital’s electronic health record. When a nurse needs a dose of warfarin or apixaban, they scan their badge, enter the patient ID, and the cabinet unlocks only the exact medication and dosage ordered. No more walking to the central pharmacy, no more handwritten orders, no more mix-ups between similar-looking pills. The system logs every single transaction—who took what, when, and for whom. That’s why they’re so critical for tracking anticoagulant use, managing high-risk drugs like opioids, and ensuring compliance with safety protocols. They also help control inventory, reducing waste and overstocking of expensive meds like semaglutide or lamotrigine.
These systems don’t just help nurses—they protect patients too. A study from the Institute of Medicine found that medication errors harm over a million people in U.S. hospitals each year. Many of those errors happen during the final steps: picking, preparing, or giving the drug. Automated dispensing cabinets cut that risk by removing human guesswork. They also prevent unauthorized access. Think about it: if a nurse needs a dose of digoxin or prednisone at 3 a.m., the cabinet gives them exactly what’s prescribed, not a random bottle from a drawer. And if someone tries to take more than their allocation, the system flags it instantly.
They’re not perfect, though. Some nurses say they slow things down when the system glitches. Others worry about over-reliance—what if the power goes out? That’s why most hospitals still keep backup supplies and manual protocols. But overall, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. From large urban hospitals to small rural clinics, automated dispensing cabinets are becoming the norm because they make medication management safer, smarter, and more transparent.
Below, you’ll find real-world guides on how these systems connect to drug safety, how they’re used with anticoagulants like apixaban, and how hospitals manage high-risk meds like methotrexate or insulin using this technology. Whether you’re a nurse, pharmacist, or just curious about how hospitals keep patients safe, these posts break it down without the jargon.