Pyxis and Omnicell: Automated Medication Systems Explained
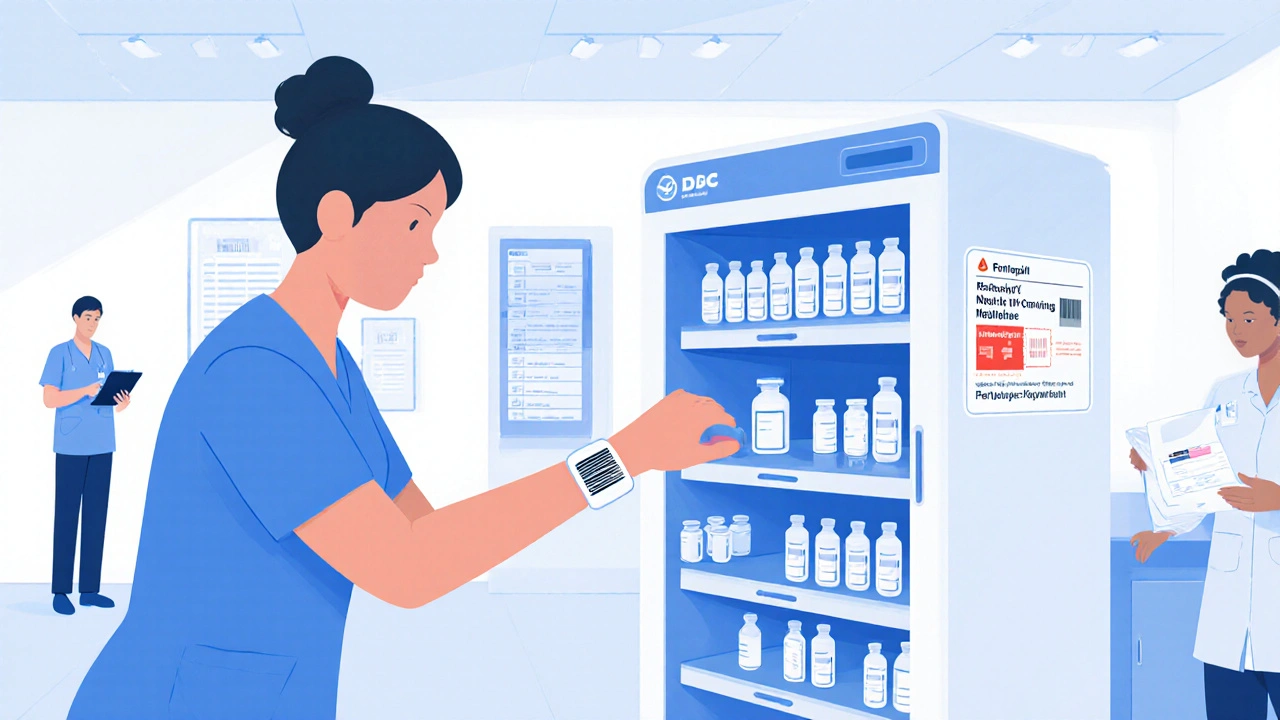
When hospitals need to get the right drug to the right patient at the right time, they often turn to Pyxis, an automated medication dispensing system used in hospitals to reduce errors and improve workflow. Also known as MedStation, it's a smart cabinet that locks and unlocks based on user credentials and patient orders. Omnicell, another major player in pharmacy automation, offers similar solutions with added inventory tracking and analytics for large healthcare networks. Also known as Omnicell XT, it’s used in both hospitals and retail pharmacies to manage everything from IV bags to controlled substances. Both systems are designed to cut down on human mistakes—like giving the wrong dose or the wrong drug—which still cause thousands of preventable injuries each year.
These systems don’t just store pills. They track every pill taken, who took it, when, and why. Nurses scan a patient’s wristband, the system verifies the medication matches the electronic order, and only then does it unlock the correct drawer. If something doesn’t line up, it won’t open. That’s not just convenience—it’s safety. Hospitals using Pyxis or Omnicell report fewer medication errors, less waste, and better compliance with regulations. They also help with staffing shortages. A nurse who used to spend 20 minutes walking to the pharmacy and waiting in line can now get meds in under a minute.
These aren’t just machines for big hospitals. Even small clinics and long-term care facilities are adopting them because the cost of a single error—like giving a patient the wrong blood thinner—can run into hundreds of thousands of dollars in legal and medical costs. Pyxis and Omnicell also connect to hospital information systems, so when a doctor changes a prescription, the cabinet updates automatically. No more handwritten orders lost in transit. No more confusing labels.
What you’ll find in the posts below are real-world examples of how these systems are used, what goes wrong when they’re misconfigured, how staff are trained to use them, and why some pharmacies still resist switching from manual processes. You’ll also see how they tie into broader topics like drug interactions, inventory control, and patient safety protocols. Whether you’re a pharmacist, nurse, hospital admin, or just curious about how meds get from the warehouse to your bedside, this collection gives you the practical details—not the marketing fluff.