Medication Side Effects
When dealing with medication side effects, the unwanted reactions a drug can cause in the body. Also known as adverse drug reactions, it can range from mild nausea to serious organ damage.
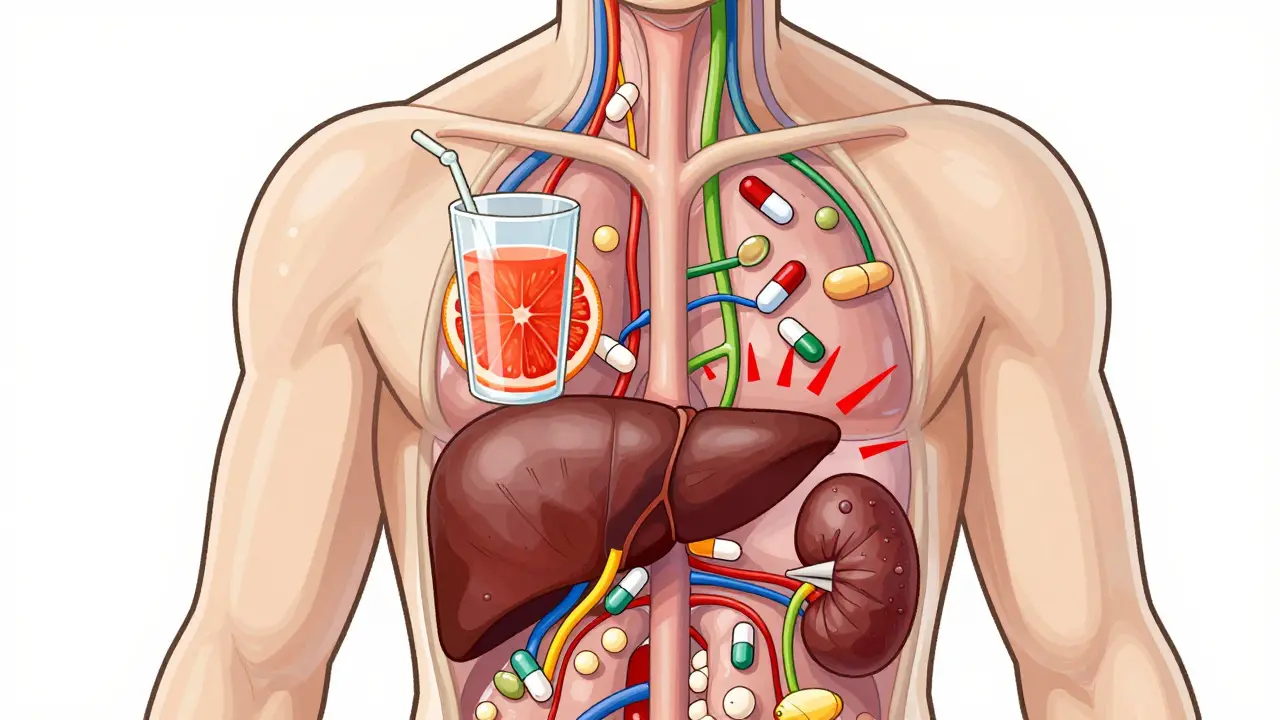
Understanding medication side effects starts with the type of product you use. generic medications, identical in active ingredients to brand‑name drugs but sold at lower cost often share the same side‑effect profile as their branded counterparts, yet price differences can affect adherence and therefore exposure risk. natural supplements, herbal or vitamin products marketed as safe alternatives are not exempt; many contain bioactive compounds that interact with prescription drugs, amplifying or masking typical side effects. Both categories illustrate the first semantic triple: Medication side effects encompass reactions from generic medications and natural supplements. Recognizing this overlap helps you spot red flags before they become problems.
How Different Drug Classes Shape Side‑Effect Profiles
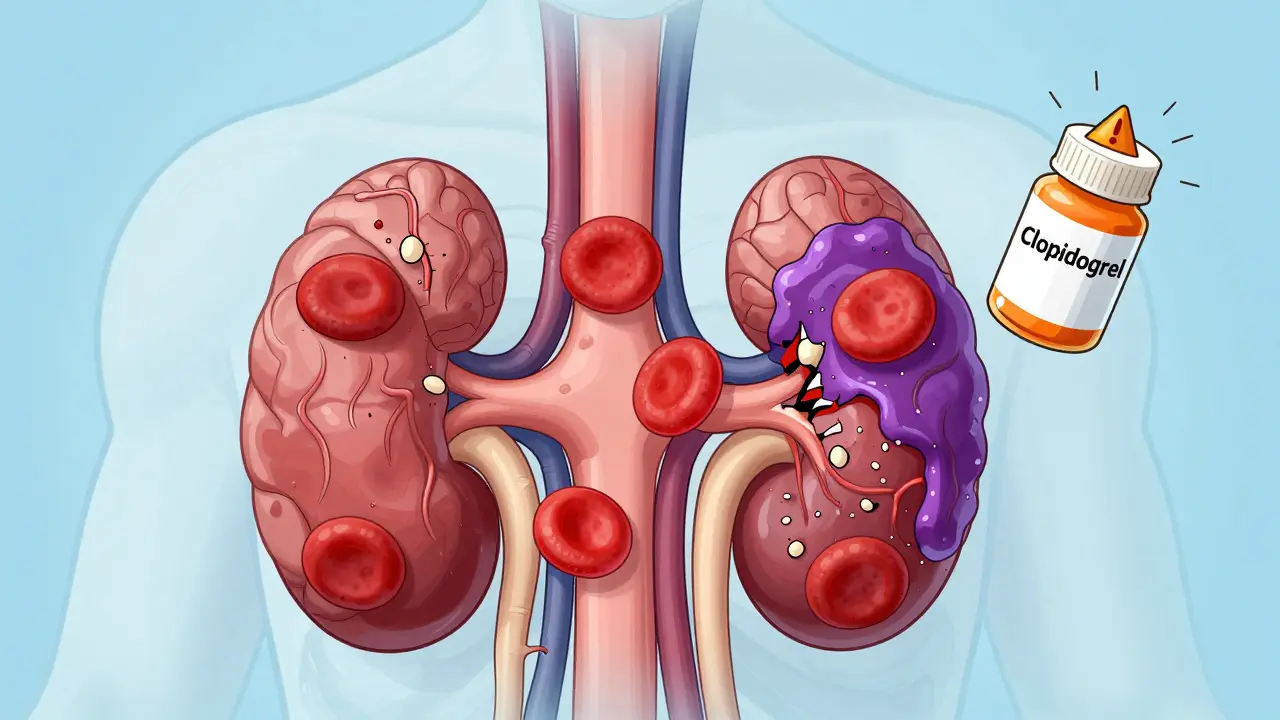
Beyond the broad categories, specific drug classes bring their own risk patterns. prescription antibiotics, agents that kill or inhibit bacteria are notorious for gut‑related issues like diarrhea or yeast overgrowth, but they can also trigger allergic reactions in susceptible individuals. over‑the‑counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may cause stomach irritation, liver strain, or kidney stress when taken in high doses or combined with alcohol. prescription steroids, potent anti‑inflammatory drugs like prednisolone can lead to weight gain, mood swings, and bone density loss over long‑term use. These three entities form a second set of semantic triples: Prescription antibiotics influence gut health; over‑the‑counter pain relievers affect liver and kidney function; prescription steroids impact metabolic balance. By mapping each class to its typical side effects, you gain a practical checklist for spotting trouble early.
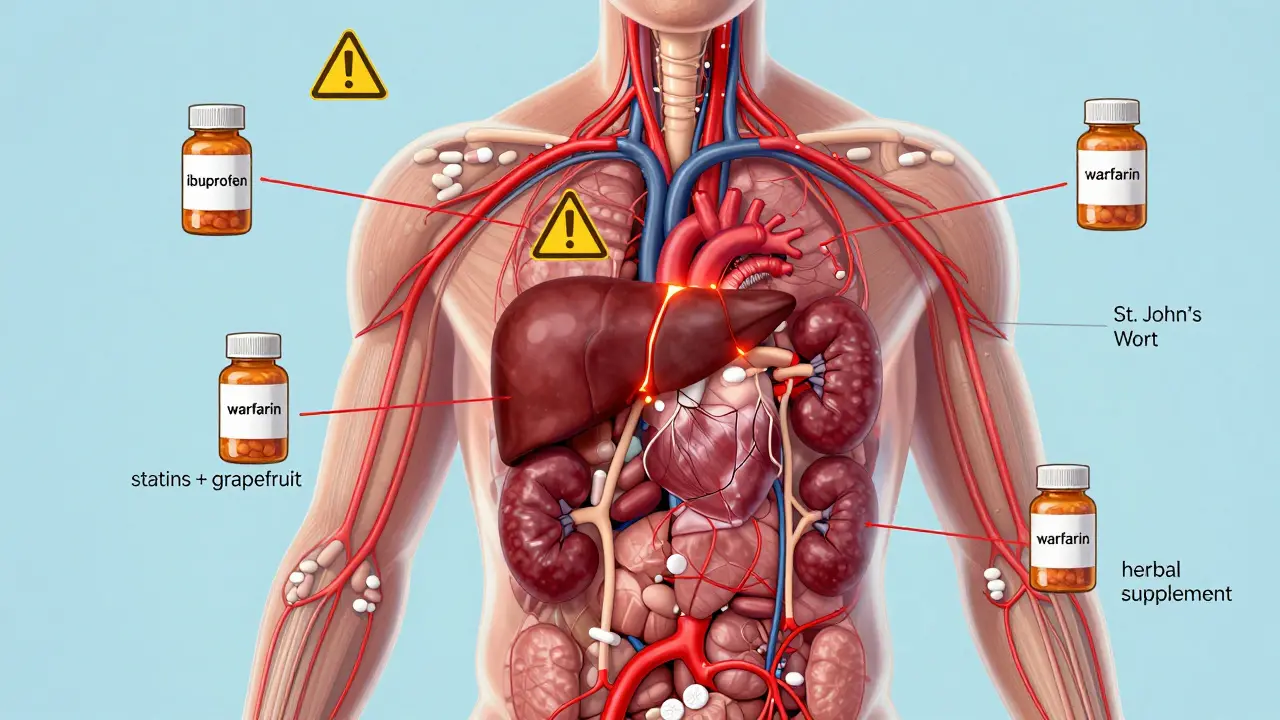
In everyday life the severity of a reaction often depends on age, existing health conditions, and other meds you’re taking. Older adults, for example, metabolize many drugs slower, making them more prone to dizziness or falls after taking certain antihistamines. People with chronic kidney disease must avoid high‑dose NSAIDs because the kidneys can’t clear the drug efficiently. Women on hormonal therapies may experience mood changes that overlap with side effects of antidepressants, creating diagnostic confusion. This third semantic triple—Patient factors such as age, organ function, and concurrent therapy shape medication side effects—highlights why a one‑size‑fits‑all warning list doesn’t work. Instead, look for patterns: sudden rash after starting a new supplement, persistent stomach pain after an antibiotic course, or unexpected sleepiness when mixing over‑the‑counter cough medicine with prescription sleep aids. Knowing the typical attributes of each drug class lets you match symptoms to likely culprits and decide when to seek professional help.
Armed with these insights, you’ll be able to read medication labels more critically, ask pharmacists targeted questions, and keep a simple side‑effect diary to track patterns over weeks or months. Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that dive deeper into specific drugs, compare generic versus brand‑name options, and explain how natural remedies interact with prescription treatments. Use the collection as a toolbox for staying ahead of unwanted reactions and making safer choices every time you reach for a pill.