Women Heart Health: Signs, Risks, and Medications That Matter
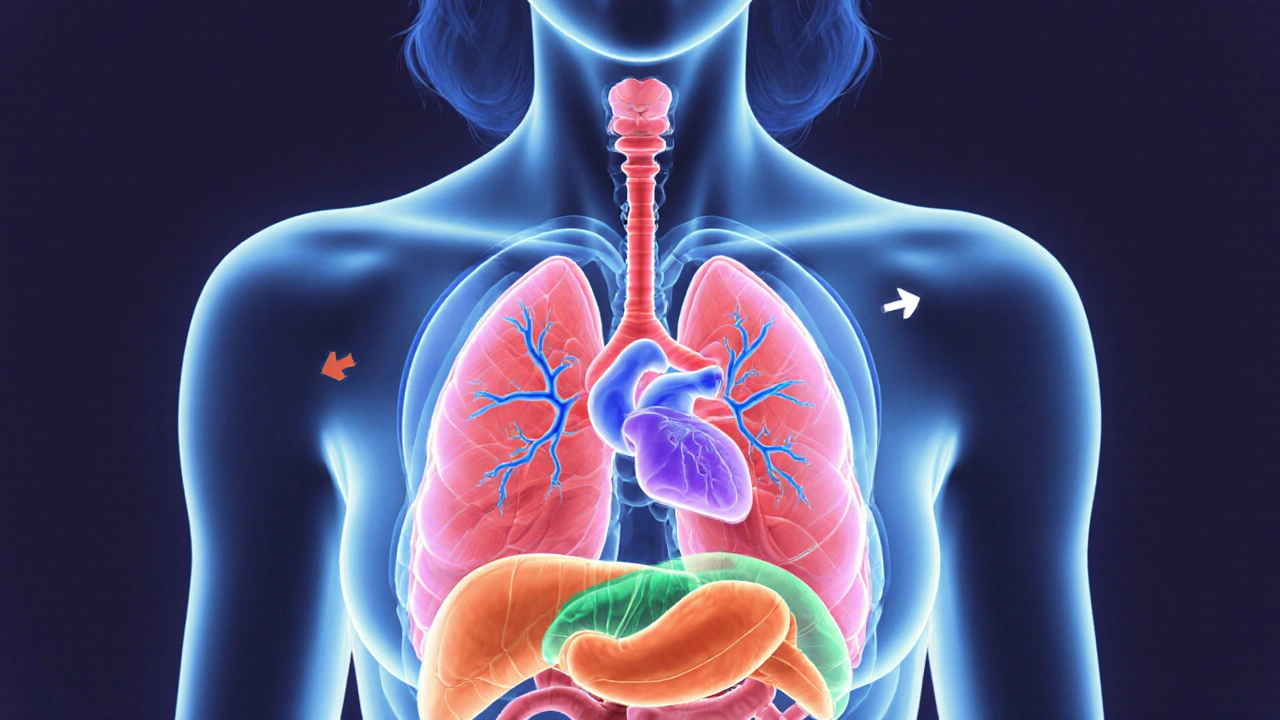
When it comes to women heart health, the leading cause of death for women worldwide, often mistaken for a man’s issue. Also known as cardiovascular disease in women, it doesn’t always show up as chest pain—it might be fatigue, nausea, or back pain that gets ignored until it’s too late. Heart disease kills more women than all cancers combined, yet most women don’t realize their symptoms are different from men’s. A 2023 study in the Journal of the American Heart Association found that over 60% of women hospitalized for heart attacks didn’t have classic chest tightness—they had jaw pain, dizziness, or sudden exhaustion. That’s why knowing the signs isn’t optional—it’s life-saving.
Digoxin, a cardiac glycoside used for heart failure and irregular heart rhythms, is still prescribed to women with diastolic heart failure, especially those over 65. But it’s not the only option. Furosemide, a loop diuretic that helps reduce fluid buildup, is often used alongside it to manage swelling and shortness of breath. And when angina strikes, nitroglycerin, a fast-acting vasodilator that opens blood vessels to the heart, can be the difference between a minor episode and a full-blown attack. These aren’t just drugs—they’re tools that fit specific needs in women’s bodies, which respond differently to medication than men’s due to hormones, body size, and metabolism.
Many women take blood pressure pills or diuretics for years without knowing how they affect their heart long-term. Furosemide might help with swelling, but it can also lower potassium too much—something that’s especially risky for older women. Nitroglycerin works fast, but if you’re using it daily, your body might start to tolerate it. And digoxin? It’s old but still used because it helps control heart rate in atrial fibrillation, a condition more common in women after menopause. The key isn’t just taking the right pill—it’s knowing why you’re taking it, and when to ask for alternatives.
Below, you’ll find real comparisons of medications women actually use—what works, what doesn’t, and what your doctor might not tell you. From how torsemide stacks up against furosemide, to why nitroglycerin is still the go-to for sudden chest discomfort, these posts cut through the noise. No fluff. No guesswork. Just what matters for your heart.