Gene-Drug Interactions: How Your DNA Affects Medication Safety and Effectiveness
When you take a pill, your body doesn’t treat it the same way everyone else’s does. That’s because of gene-drug interactions, the way your genetic makeup changes how your body absorbs, breaks down, or responds to medications. Also known as pharmacogenomics, this field explains why one person gets relief from a drug while another suffers side effects—even with the same dose. It’s not about being allergic. It’s about your DNA.
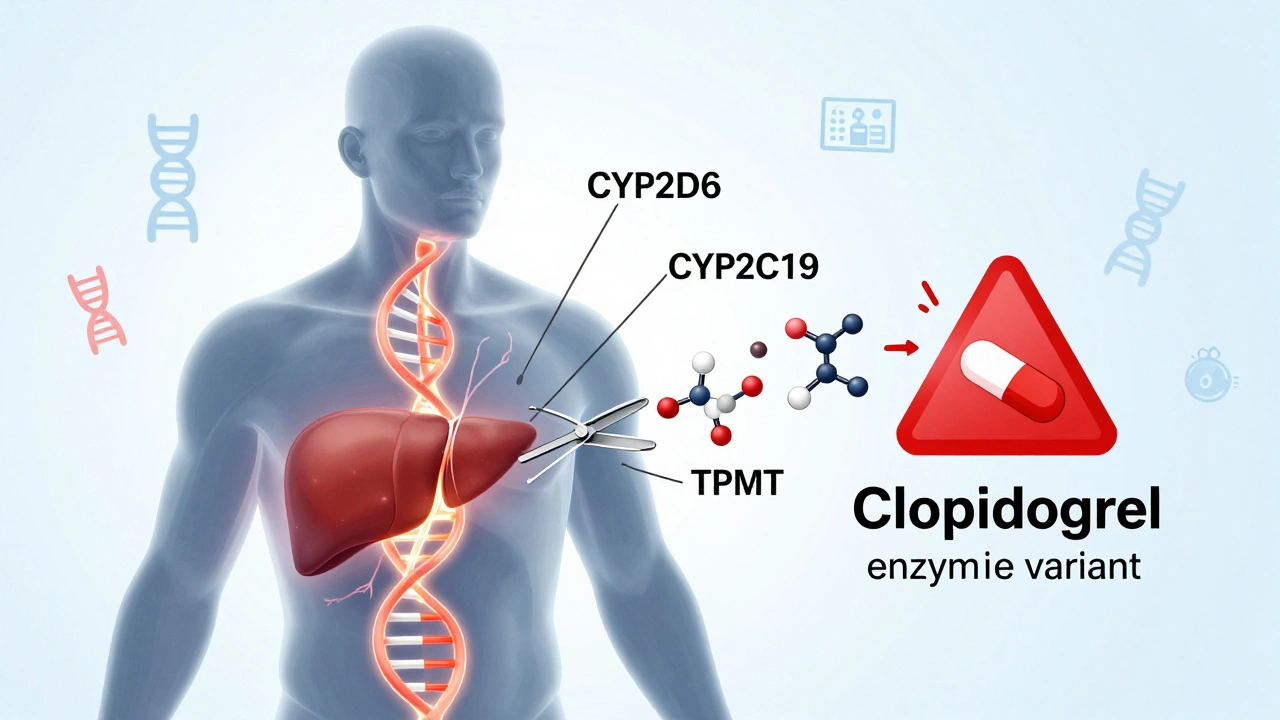
Some people have genes that make them process drugs too fast, leaving the medication ineffective. Others break them down so slowly that even a normal dose builds up to toxic levels. For example, a common blood thinner like warfarin can be dangerous if your genes make you a slow metabolizer. The same goes for antidepressants, painkillers, and even chemo drugs. Studies show up to 90% of people carry at least one gene variant that affects how they respond to at least one medication. That’s not rare. That’s normal.
These interactions aren’t just theoretical. They show up in real life: a patient on statins gets muscle damage because of a gene that blocks drug clearance. Another person takes clopidogrel for a stent, but it doesn’t work because their body can’t activate it. These aren’t mistakes. They’re predictable outcomes of your biology. That’s why genetic testing, a simple cheek swab or blood test that checks key drug-metabolizing genes is becoming part of routine care. It’s not science fiction—it’s used in hospitals to guide dosing for heart drugs, epilepsy meds, and cancer treatments.
And it’s not just about what you take. It’s about what you don’t take. Certain foods, supplements, and other drugs can block or boost how your genes work. Grapefruit, for instance, can shut down a liver enzyme that breaks down dozens of medications. That’s why a drug metabolism, the process your liver uses to break down and eliminate medications profile matters as much as your medical history.
What you’ll find below are real stories and science-backed guides on how these interactions play out. From chemotherapy and blood thinners to antidepressants and pain meds, the posts here show you how gene-drug interactions affect treatment, why some generics behave differently, and how pharmacists and doctors use this info to keep you safe. No fluff. No theory. Just what you need to know to ask the right questions and get better care.